September 2024
HIGHLIGHTS
International reserves increased from USD 37.2 billion to USD 42.3 billion in August 2024.
On September 19, the NBU Board decided to keep the key interest rate at 13%.
Year-on-year, inflation rose from 5.4% to 7.5% in August 2024.
On September 11, an agreement was reached at the staff level on the fifth review of the Extended Fund Facility arrangement with the IMF. Ukraine will have access to SDR 834.8 million (equivalent to about USD 1.1 billion).
On September 14, the Government of Ukraine presented the budget for 2025. We estimate consolidated budget revenues at 40.3% of GDP, including grants of about 1% of GDP, and consolidated expenditures at 59.9% of GDP, including 26.3% for security. The budget deficit amounts to 19.6% of GDP.
Review of the arrangement with the IMF.
On September 11, a staff-level agreement was reached on the fifth review of the Extended Fund Facility arrangement with the IMF. Ukraine will have access to SDR 834.8 million (equivalent to about USD 1.1 billion).
According to the Fund’s forecast, economic growth in Ukraine will slow in the second half of 2024 due to the consequences of Russian attacks on energy infrastructure, the impact of the war on the labor market, and the level of business expectations. The forecast for real GDP growth in 2024 is 3%, and inflation is expected to reach 9%. Addressing the issue of power shortages before winter is critical and will require coordinated efforts, including from international partners. The Fund forecasts economic growth of 2.5-3.5% in 2025. At the same time, the risks to the forecast are extremely high.
The Fund noted:
”The 2025 Budget needs to respect financing constraints and debt sustainability objectives, and determined domestic revenue mobilization efforts are critical. Timely and predictable external financial support, on terms consistent with debt sustainability, remains indispensable for maintaining economic stability.
Tax revenues need to increase in 2025 and beyond to create space for critical spending, to preserve essential buffers and restore fiscal sustainability. Achieving this will require the implementation of permanent tax policy measures and relentless efforts to close existing opportunities for tax evasion, improve compliance, and combat the shadow economy, in line with the National Revenue Strategy (NRS). Legislation to reform the Customs code should confirm the central role of the Finance Ministry in overseeing customs, while robust processes should be established for selecting a permanent head of customs as well as other key leadership roles.”
ECONOMIC SITUATION
- GDP growth
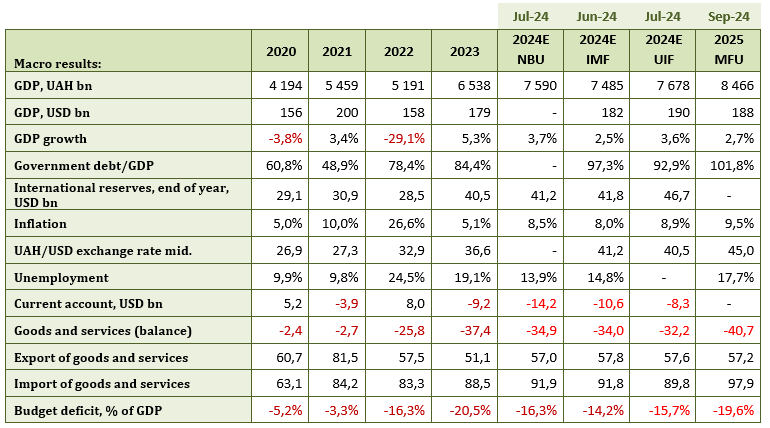
According to the Ministry of Economy, GDP grew by 2.7% in July. Several factors contributed to this growth: early harvest, stable operation of the sea corridor, and gradual growth in consumer demand.
The Ministry of Economy estimates that GDP grew by 4% between January and July this year.
Source: NBU.
2. Inflation.
Inflation in the consumer market in August 2024 compared to July 2024 amounted to 0.6% and 4.9% since the beginning of the year. In the consumer market, prices of food and non-alcoholic beverages increased by 0.9% in August. Eggs and vegetables rose the most (by 7.1% and 5.2% respectively). Alcoholic beverages and tobacco rose by 0.8%, driven by a 1.4% increase in tobacco prices. Clothing and footwear fell by 2.9%, with footwear down 3.4% and apparel down 2.4%. Transportation prices rose by 0.6%, mainly due to a 1.2% increase in the price of motor vehicles, a 0.6% increase in the price of motor vehicle passenger transport, and a 0.5% increase in the price of fuel and oil.
Year-on-year, inflation rose from 5.4% to 7.5% in August 2024.
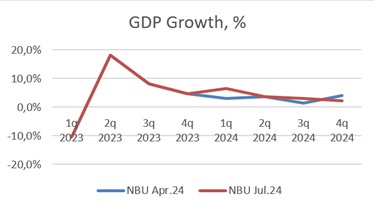
Industrial inflation reached 33% year-on-year in July. This was mainly due to higher electricity prices.
Source: Ukrainian energy market, Market Operator.
In annual terms, electricity prices for industrial consumers have increased by 30-35% per year and have doubled in the last two years. This puts pressure on the competitiveness of Ukrainian goods in foreign markets, increasing expectations of devaluation and higher consumer inflation at the end of 2024 and 2025.
3. NBU interest rate
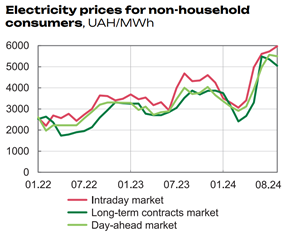
On September 19, the NBU Board decided to keep the key interest rate at 13%. The decision is to gradually reduce inflation to a target of 5% in the coming years and will support the stability of the foreign exchange market.
The National Bank introduced a highly adaptive monetary policy in order to improve the dynamics of macroeconomic indicators in order to assess the changes in the balance of risks for inflation, the stability of the foreign exchange market and economical development.
In July 2024, the interest rate on new hryvnia loans for the corporate sector increased from 15.2% to 16.5%, and for households decreased from 34.1% to 34%.
NBU forecast for the key interest rate. July 2024
BUDGET
1. Budget expansion by UAH 500 billion.
On September 18, the Parliament of Ukraine adopted draft law No. 11417, which provides for an increase in security spending by 500 billion hryvnias by the end of the year.
On September 17, the Parliament of Ukraine voted in the 1st reading on the revised version of the draft law 11416-d, which, in addition to increasing the military tax from 1.5% to 5% on salaries, +1% on the income of the 3rd group of sole proprietors, +10% of the minimum wage, and on the income of the 1-2-4 groups of sole proprietors, also includes an advance payment of 50% of bank profits in 2024. According to our estimates, this could bring an additional UAH 70-80 billion to the 2024 budget.
The budget deficit is to be covered by domestic borrowing at rates of 15-17% in hryvnia, which will significantly increase debt servicing costs.
2. Budget execution
In 7 months of 2024, the consolidated budget was closed with a deficit of UAH 700.1 billion (UAH 135 billion in July). This is UAH 190.2 billion more than in 7 months of 2023 (UAH 509.9 billion).
Nevertheless, tax revenues in 7 months of 2024 are already UAH 282 billion higher than in 2023.
At the same time, the surplus of local budgets for seven months amounted to UAH 63 billion, and the state budget deficit amounted to UAH 763 billion.
As of August 1, the balances on the accounts of the state and local budgets decreased from UAH 59 billion in June to UAH 35 billion, which means that to finance the expenditures of the state budget in July, the state budget, in reality, borrowed UAH 28 billion from local budgets and has no funds of its own on its accounts.
3. External financing
Ukraine received USD 24.6 billion in external financing in the first eight months. Of this, USD 6.6 billion were grants, and USD 17.9 billion were loans.
In August, the budget received USD 3.9 billion from the US and EUR 4.2 billion (USD 4.6 billion) from the EU, of which EUR 1.5 billion was a grant. This solves the budget’s liquidity problem.
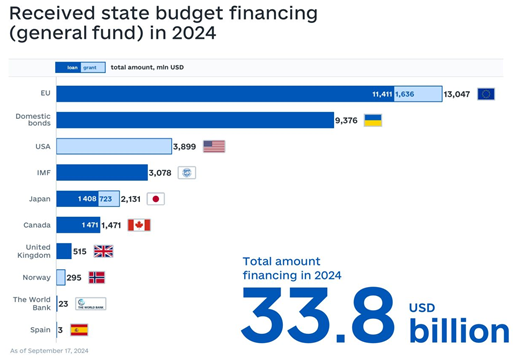
Source: Ministry of Finance of Ukraine
4. Public debt
As of August 1, Ukraine’s public and guaranteed debt amounted to USD 155 billion (+ USD 10 billion for seven months of 2024).
Ukraine completed restructuring its sovereign and government-guaranteed Eurobonds for USD 20.5 billion. The restructuring included the exchange of thirteen series of Ukravtodor’s sovereign Eurobonds and one series of Ukravtodor’s government-guaranteed Eurobonds for eight new series of Eurobonds with a nominal value of USD 15.2 billion.
As a result of this transaction, Ukraine’s public and publicly guaranteed debt was reduced by approximately USD 5.3 billion.
However, if GDP growth exceeds 4.3% in 2028, Ukraine will be charged an additional 12% of its debt, amounting to approximately USD 2.8 billion. In this case, public and publicly guaranteed debt will be reduced by only USD 2.5 billion.
In addition, we believe that the Ministry of Finance is hiding other restructuring agreements. Officially, the Ministry of Finance will pay a commission of USD 246 million (1.25%) of the restructuring amount, or about UAH 10 billion. At the same time, the Ministry of Finance’s plan to pay interest on other liabilities was changed by UAH 26 billion as of August 2024. This means an additional interest liability of USD 650 million.
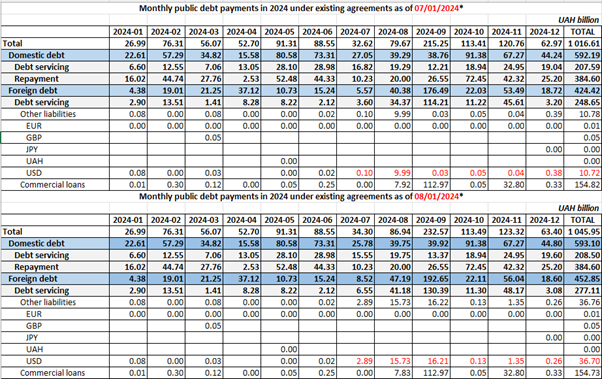
Source: Ministry of Finance of Ukraine
5. Budget for 2025
On September 14, the Government of Ukraine presented the budget for 2025. We estimate consolidated budget revenues at 40.3% of GDP, including grants of about 1% of GDP, and consolidated expenditures at 59.9% of GDP, including 26.3% for security. The budget deficit stands at 19.6% of GDP.
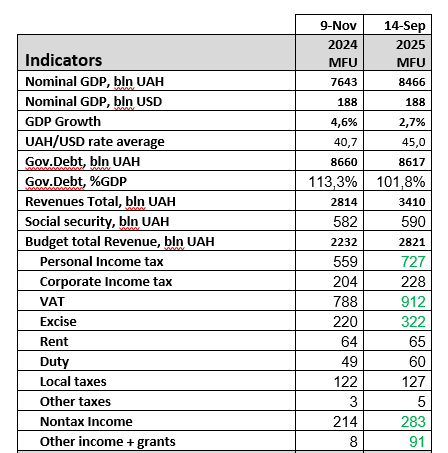
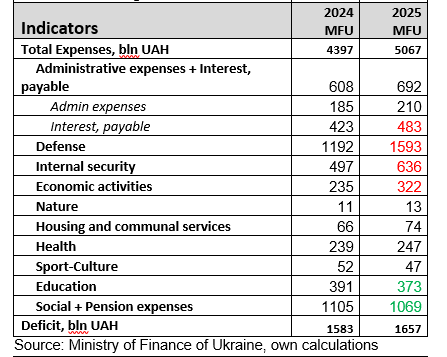
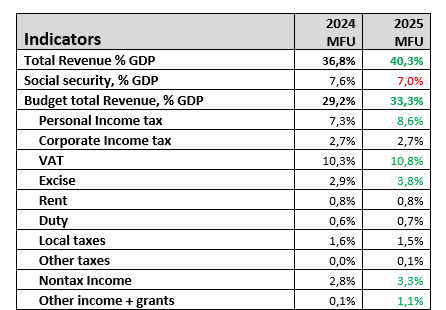
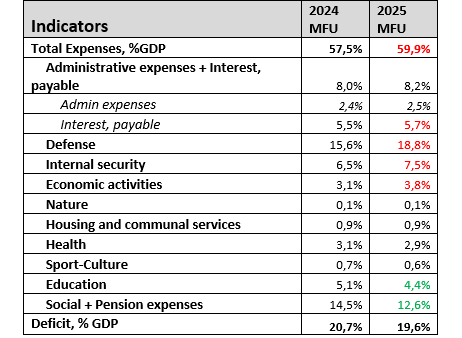
Source: Ministry of Finance of Ukraine, own calculations
The 2025 budget assumes economic growth of 2.7% of GDP. Consumer inflation of 9.5%. An increase in the average hryvnia-dollar exchange rate from 40.8 to 45 and a rate of 48 hryvnia to the euro in 2025.
Budget 2025 is a military budget for the whole year 2025. The budget plans to increase security spending from 22.1% to 26.3% of GDP. However, not all of this is security spending. In 2023-2024, Western military aid was estimated at 10-12% of GDP in addition to Ukraine’s own spending. Ukraine is not confident that arms supplies from the West will be sufficient, so it is increasing its own arms production and plans to spend at least USD 10 billion.
A shift in priorities. While security was the top priority in 2022-2023, followed by social welfare, the second priority in the 2025 budget is economic spending, which may indicate an increase in corruption or the independent restoration of critical infrastructure facilities. The projected increase in spending on economic affairs, which does not include military spending, is from UAH 235 billion to UAH 332 billion.
Huge debt servicing costs – UAH 482 billion or 5.7% of GDP. We believe these costs have a reserve in UAH 50-70 billion expenditures. This is especially true given the restructuring of commercial debt in August 2024.
Increased tax burden on the economy. In the 2025 budget, the government has taken into account an increase in the military tax of 11416-d (an increase of about 1.3% of GDP). Increased excise taxes on fuel and tobacco products.
The budget deficit is 19.6% of GDP. The main source of financing is 38.4 billion in Western aid. At the same time, there are agreements with the EU, IMF, and IBRD for about USD 17.8 billion. The rest is not yet determined. Ukraine is awaiting a decision on a USD 50 billion loan from the G7, allowing it to bridge the end of 2024 and cover all of 2025.
Balance of payments
1. Balance of payments in July of 2024.
Trends in the balance of payments that deserve attention include:
- A deterioration in the trade balance was particularly evident in July 2024. The trade deficit in goods reached a record high of USD 3 billion. Add this to the USD 600 million trade imbalance in services in July, and we have a record negative balance of USD 3.6 billion since January 2023. This was caused by both a decline in exports to USD 2.9 billion from a baseline of USD 3.3 billion in the first five months and record imports of goods, which reached USD 6 billion. The import surge was caused by the continued devaluation of the local currency to 41.5 hryvnia to the dollar, with expectations of further devaluation encouraging business purchases, increased electricity imports, and government plans to sharply increase taxes, including on car purchases.
- The number of migrant workers’ remittances to Ukraine. These have already fallen to around USD 700 million per month. A year ago, it was USD 900 million per month.
- Households buying foreign currency for cash. Foreign exchange purchases accelerated again to USD 1.44 billion per month.
- Low level of Western financing. Ukraine only received USD 2.2 billion in funds from the IMF.
Thus, the balance of payments in July 2024 was negative, and international reserves decreased from USD 37.9 billion to USD 37.2 billion. Since the beginning of the year, they have dropped by USD 3.3 billion from USD 40.5 billion.
2. Hryvnia exchange rate
In August and early September, the hryvnia exchange rate against the US dollar stabilized in the range 41-41.5 hryvnia to the dollar.
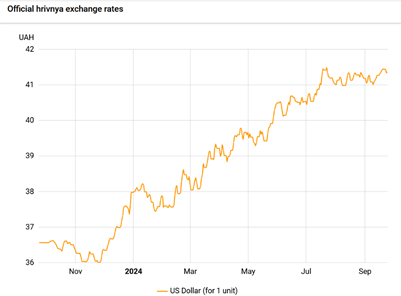
Hryvnia exchange rate against the US dollar over 12 months. Source: NBU.
We believe the devaluation in September will be mild and controlled by the NBU. The NBU may keep the exchange rate in the 41-41.5 range, but there is a risk that the devaluation will be used as a factor to partially solve the budget problems.
International reserves
International reserves increased from USD 37.2 billion to USD 42.3 billion in August 2024. The net sale of foreign currency by the NBU in August amounted to USD 2,695.5 million. This is a decrease of 18.4% compared to July. The government’s foreign currency accounts with the NBU received USD 8,465 million. Of this amount, USD 4,552.9 million. USD 4,552.9 million was received from the European Union, and USD 3,899 million was received from the United States.
USD 724.1 million was paid for the servicing and repayment of the public debt in foreign currency, of which:
- USD 266 million – debt servicing and repayment to the World Bank;
- USD 239.9 million – payments related to legal transactions (government bonds);
- USD 130.1 million – payments on government derivatives;
- USD 88.1 million – payments to other international creditors.
In addition, Ukraine paid USD 392.4 million to the International Monetary Fund.
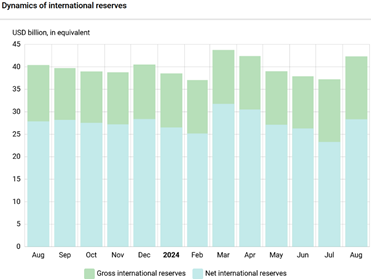
Change in international reserves over the past 12 months. Source: NBU.
FORTHCOMING EVENTS
Late September: Updated IMF forecast based on the results of the fifth review of the arrangement with Ukraine.
October 10: Updated forecast of the Ukrainian Institute for the Future for 2024: Economy, Budget, Balance of Payments.


Вам також буде цікаво:
Ukraine’s Energy Sector Developments
Macroeconomic Digest of Ukraine
Macroeconomic Digest of Ukraine
Ukraine’s Energy Sector Developments
Macroeconomic Digest of Ukraine (August 2024)
Macroeconomic Digest of Ukraine(July 2024)